[AWS] AWS CloudFront with Signed URL
Amazon CloudFront is a fast content delivery network (CDN) service managed by AWS. It serves your contents across edge locations around the globe with high transfer speeds and low latency under secured connections.
In this post, we will set up an Amazon CloudFront distribution that serves private contents on your S3 bucket in order to speed up your content retrival while fully controlling user access permissions.
Setting up CloudFront
First, create a key pair for later use:
openssl genrsa -out cfprikey.pem 2048
openssl rsa -in cfprikey.pem -outform PEM -pubout -out cfpublic.pem
Create CloudFront public key using the public key you just created:
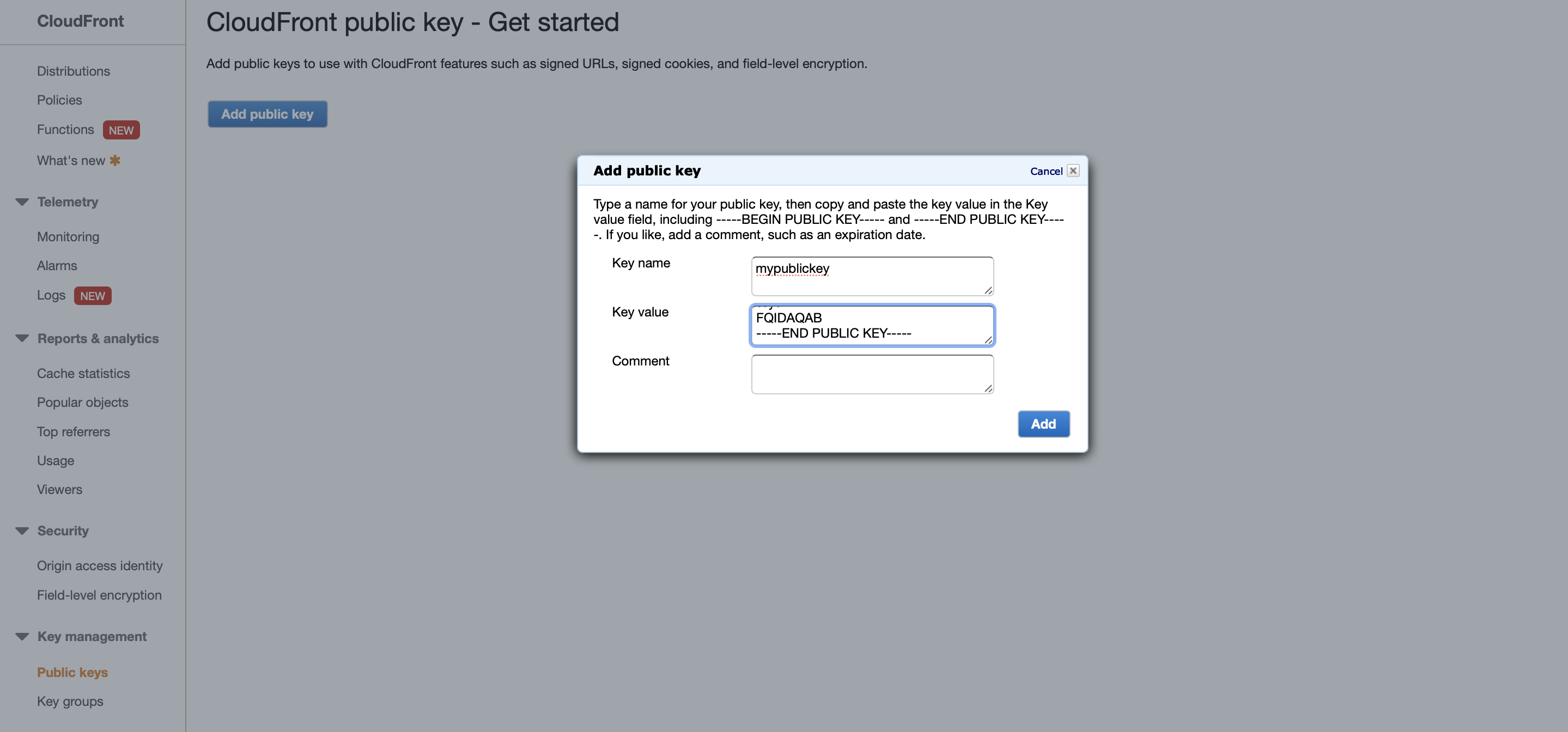
After the public key is created, it will be given a public key ID. You will need it when signing CloudFront URLs.
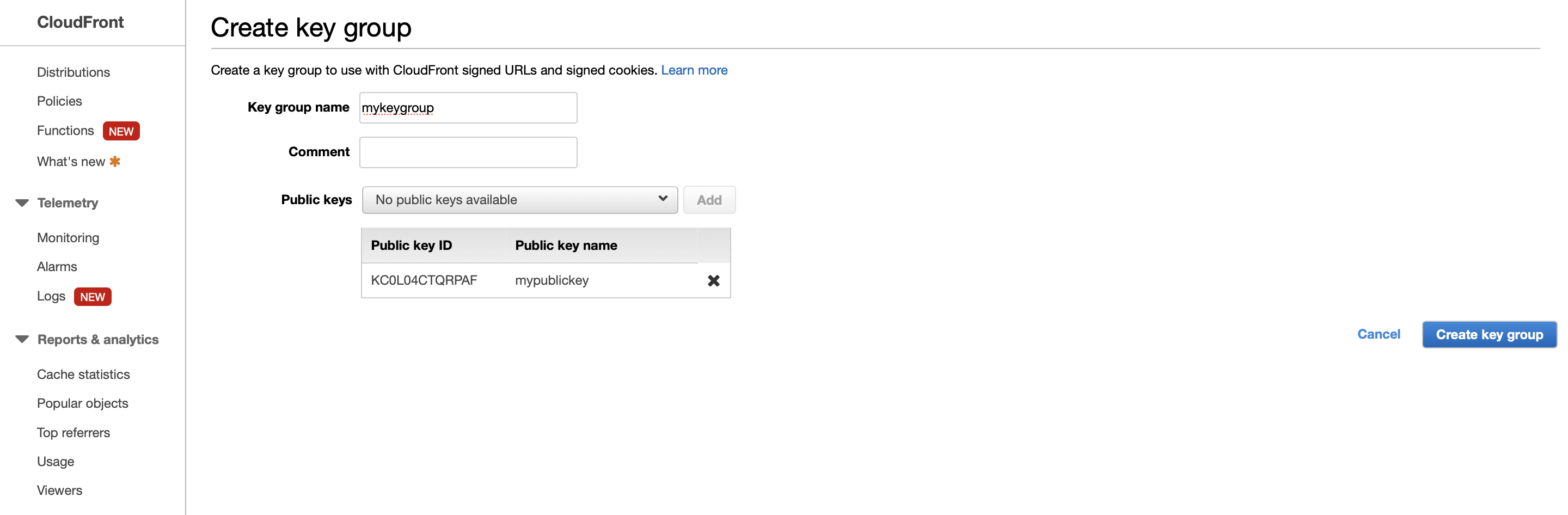
Create a key group that is associated with the CloutFront public key mypublickey:
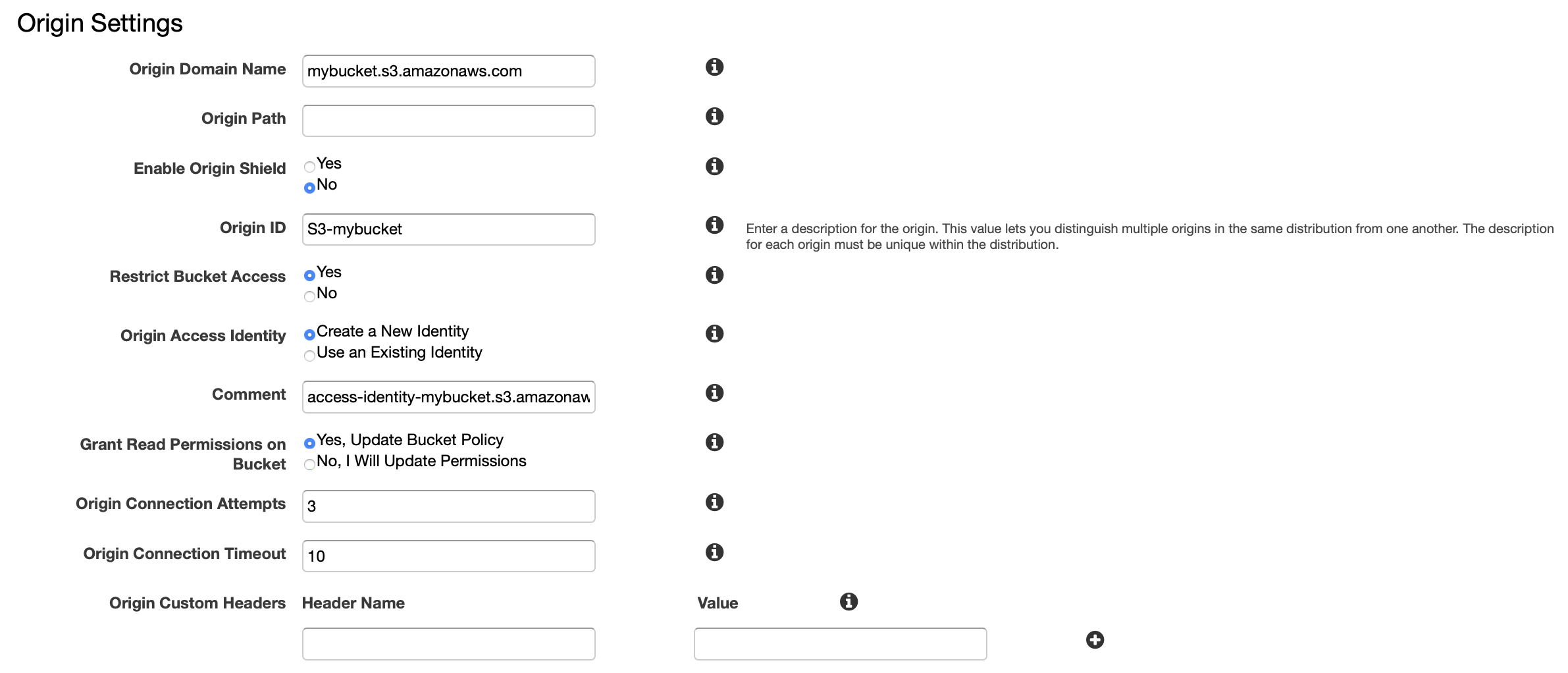
Then create a CloudFront distribution. Connect its orgin to your S3 bucket mybucket. Also, enable the CloudFront bucket access restriction and add a new CloudFront origin access identity to your S3 permission policy:
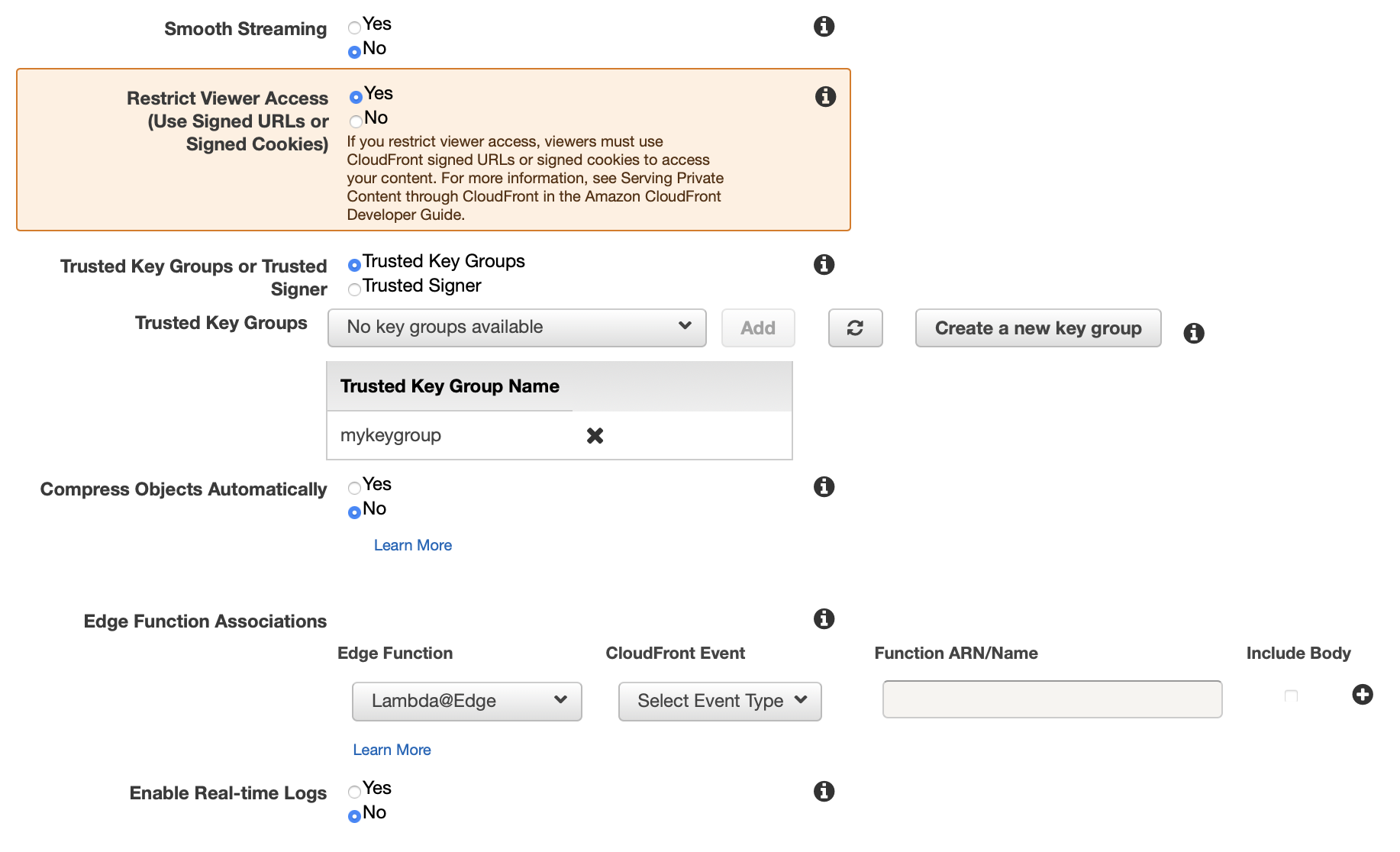
Enable the CloudFront viewer access restriction and connect it to your key group:
Check your CloudFront distribution status here. Wait until its status becomes Deployed. Then you will see the domain name of your CloudFront distribution.
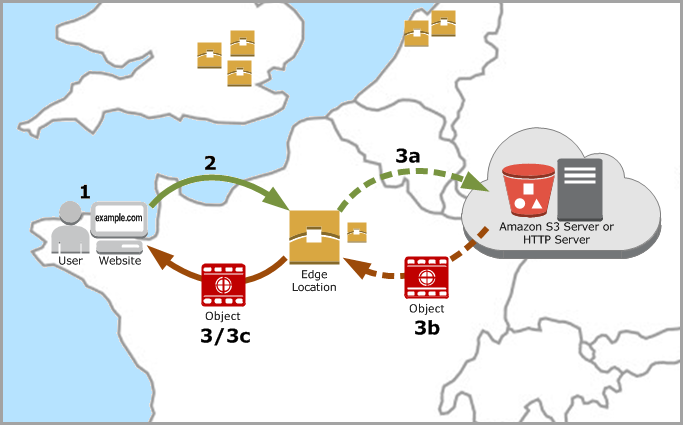
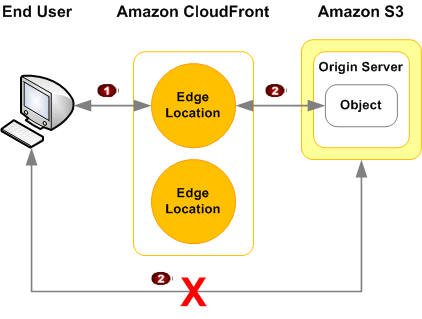
We enabled the CloudFront bucket access restriction so that clients cannot access your object using S3 URL but only CloudFront URLs.
Whenever your users access your Amazon S3 objects through CloudFront, the CloudFront origin access identity retrieves the objects on behalf of your users. If your users request objects directly by using Amazon S3 URLs, he or she will be denied. The procedure can be summarized in the following figure:
In addition, we restrict viewer access so that only requests through signed URLs are allowed to access your content. The signing mechanism works by hashing and signing one part of the URL using the private key from your public–private key pair. When someone uses a signed URL to access a file, CloudFront compares the signed and unsigned portions of the URL. If they don’t match, CloudFront doesn’t serve the file.
If you don’t restrict viewer access, all requests through CloudFront URLs are allowed to access your backend S3 objects, ie. they are public to the entire world. So please be sure to enable the viewer access restriction if you want to protect your private contents.
Signed URL Creation Example
You can see the complete source code example on my Github.
In this example, we will use Golang AWS SDK to upload hello.txt to S3 bucket mybucket with key mysubpath/hello.txt. Then we will create its signed URL, which has a 1 hour expiration. Users can only access your private content hello.txt through this signed URL.
First, create a new client session:
creds := credentials.NewStaticCredentials(accessKey, secretKey, "")
config := &aws.Config{
Credentials: creds,
Region: aws.String(s3Region),
MaxRetries: aws.Int(3),
}
session, err := session.NewSession(config)
Upload hello.txt to the S3 bucket:
fromFile, err := os.Open(uploadFrom)
if err != nil {
exitErrorf("Unable to open file %q, %v", uploadFrom, err)
}
defer fromFile.Close()
uploader := s3manager.NewUploader(session)
var output *s3manager.UploadOutput
output, err = uploader.UploadWithContext(context.Background(), &s3manager.UploadInput{
Bucket: aws.String(s3Bucket),
Key: aws.String(objKey),
Body: fromFile,
})
Sign the CloudFront object URL of hello.txt with the CloudFront public key ID and private key you created previously:
var priKey *rsa.PrivateKey
priKey, err = sign.LoadPEMPrivKey(priKeyFile)
if err != nil {
exitErrorf("err loading private key, %v", err)
}
var signedURL string
signer := sign.NewURLSigner(cfAccessKey, priKey)
rawURL := url.URL{
Scheme: "https",
Host: cfDomain,
Path: objKey,
}
signedURL, err = signer.Sign(rawURL.String(), time.Now().Add(1*time.Hour))
if err != nil {
exitErrorf("Failed to sign url, err: %v", err)
}
fmt.Printf("Get signed URL %q\n", signedURL)
The CloudFront object URL https://mycfdomain.cloudfront.net/mysubpath/hello.txt is now signed, and th result is printed in the standard output. Users can access hello.txt through this signed URL until it expires.