[AWS] Deploy Docker Containers on ECS
We are going to deploy a sample app container on Amazon ECS using Fargate, a serverless compute engine for containers. Fargate removes the need to provision and manage servers, lets us specify and pay for resources per application, and improves security through application isolation by design.
Steps
First, click get started to create a cluster from the startup template.
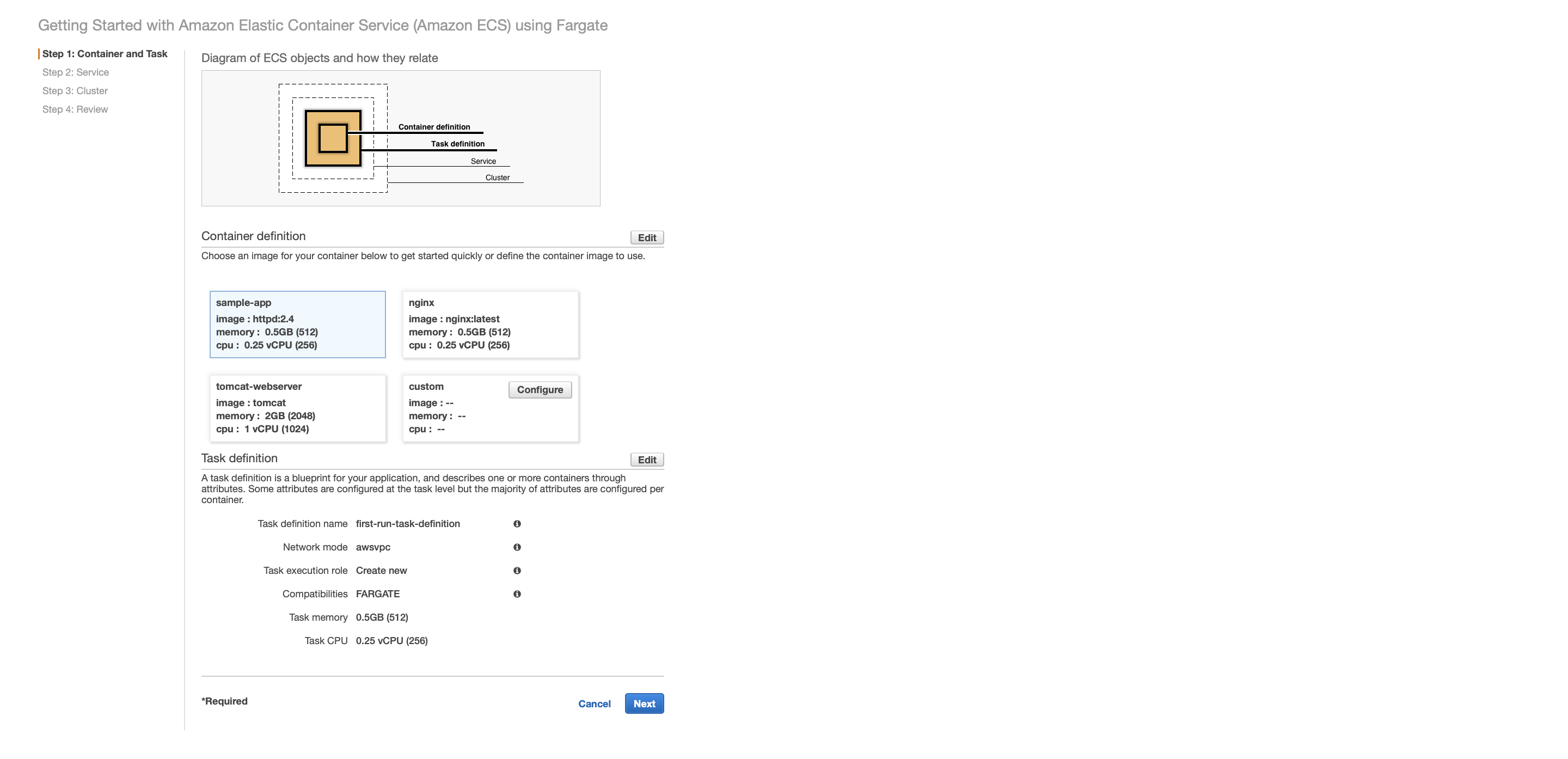
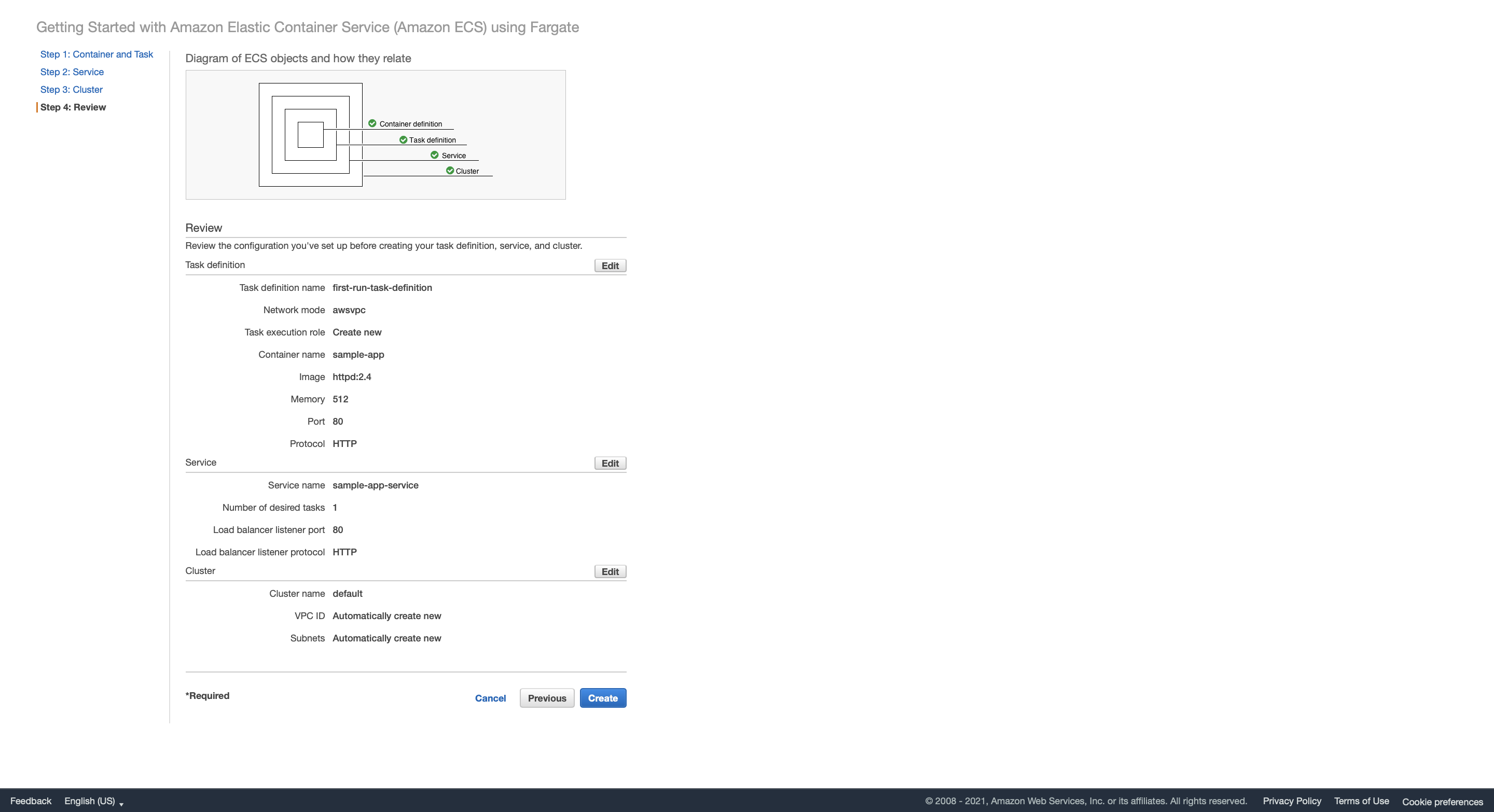
Configure container definition and task definition. Choose sample-app image and the use the default task definition. This will create a task execution role automatically, which gives right permissions to ECS tasks.
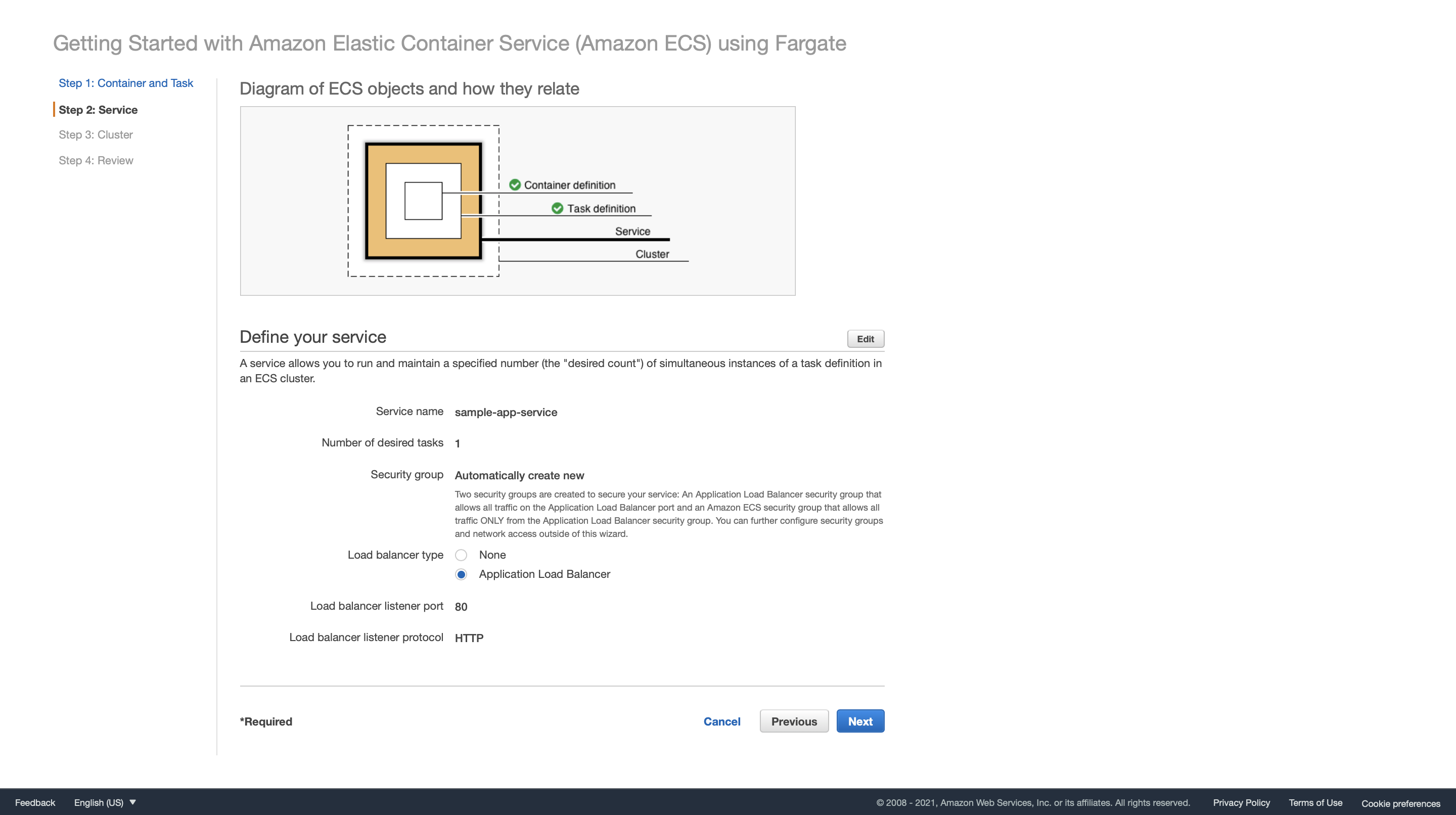
Next, define the service. A service lets us specify how many copies of task definition to run and maintain in a cluster. We can optionally use an Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) load balancer to distribute incoming traffic to containers in the service. Amazon ECS maintains that number of tasks and coordinates task scheduling with the load balancer. We can also optionally use Service Auto Scaling to adjust the number of tasks in the service. Here, we will use an Application Load Balancer (ALB) to route incoming requests to our sample app.
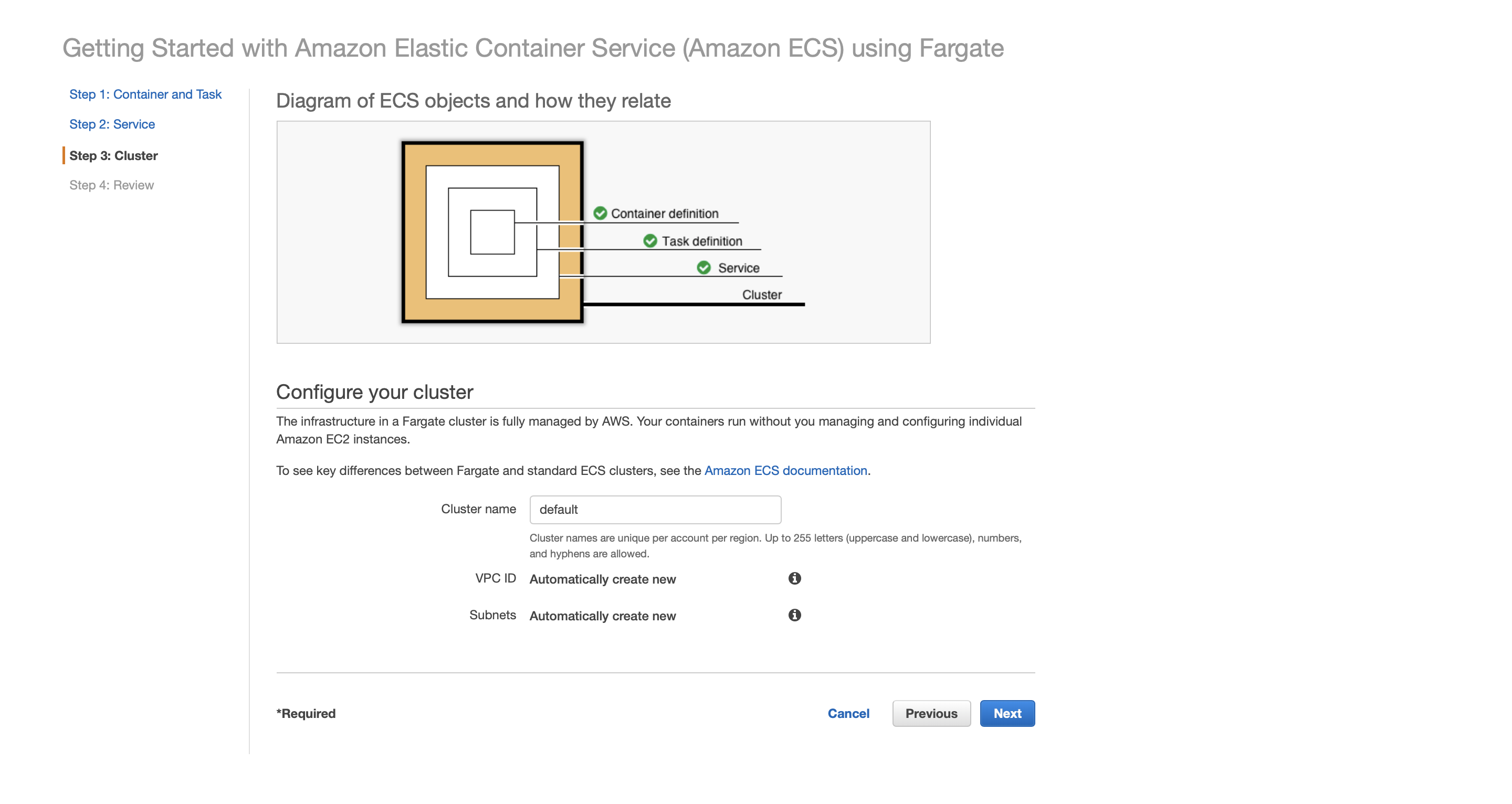
Finally, configure your ECS cluster. We could either create a new VPC and subnets automatically or attach an existed VPC to our cluster.
Overview:
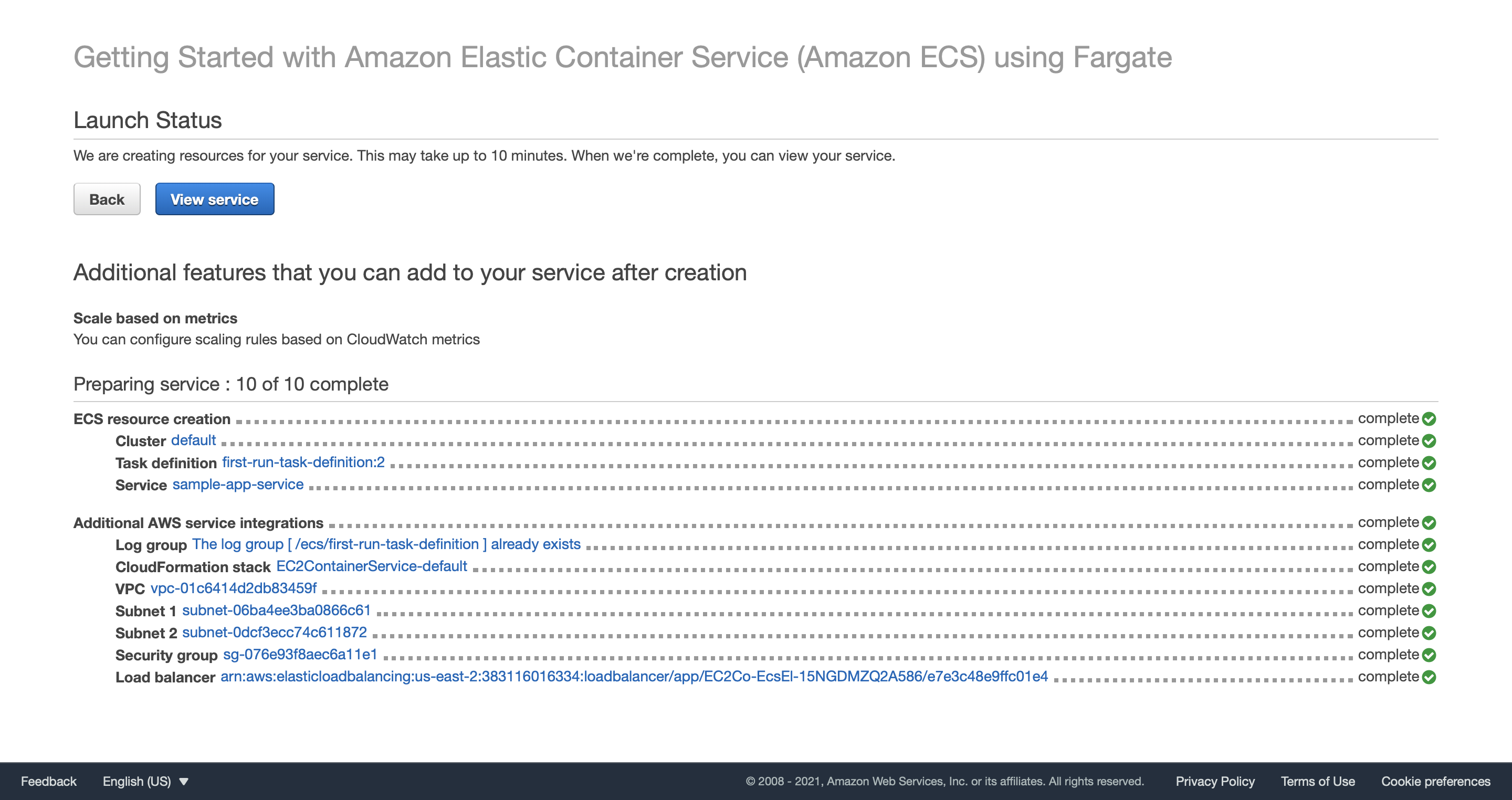
Watch the ECS cluster lauch status. The creation takes a few minutes.
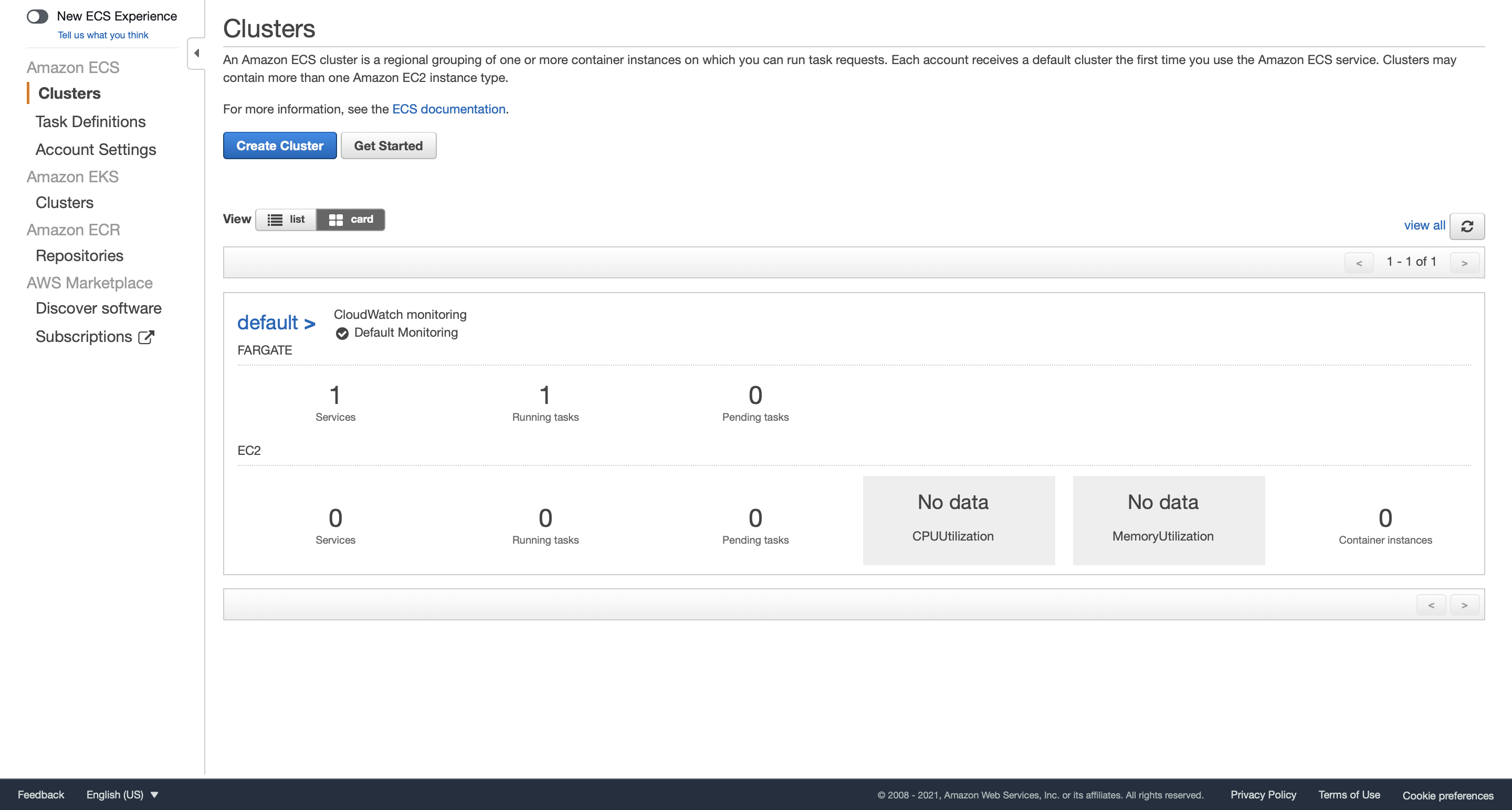
After the creation is completed, we can see that there is one service and one running task in our cluster. A task is the instantiation of a task definition within a cluster. After you have created a task definition for your application within Amazon ECS, you can specify the number of tasks to run on your cluster.
Check the service details. We can see that our task, load balancing, and networking all work successfully.
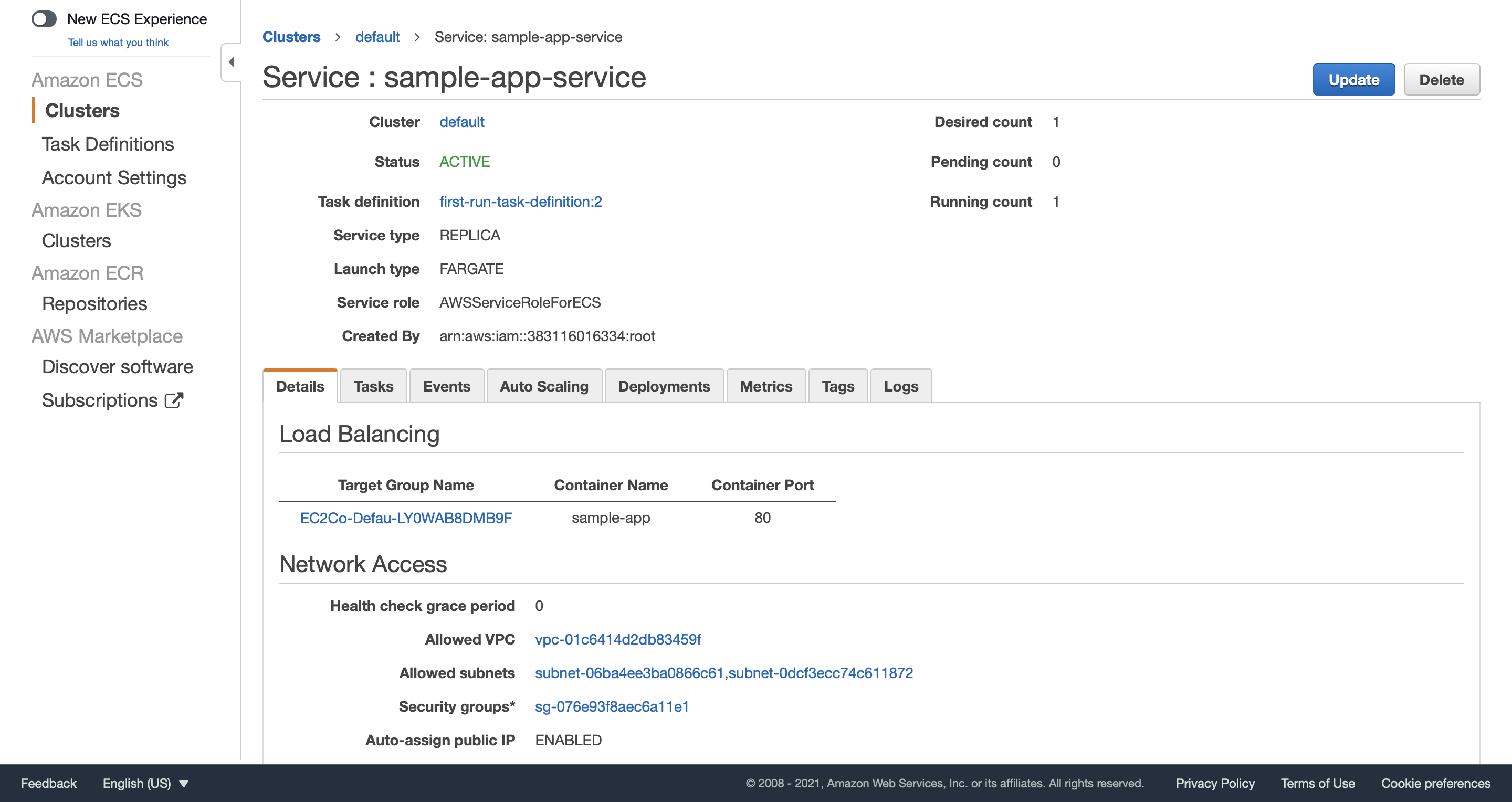
Click Tasks tab and check details of our only task. In the Network section, we can see the auto-assign public IP (18.188.40.78) of our container.
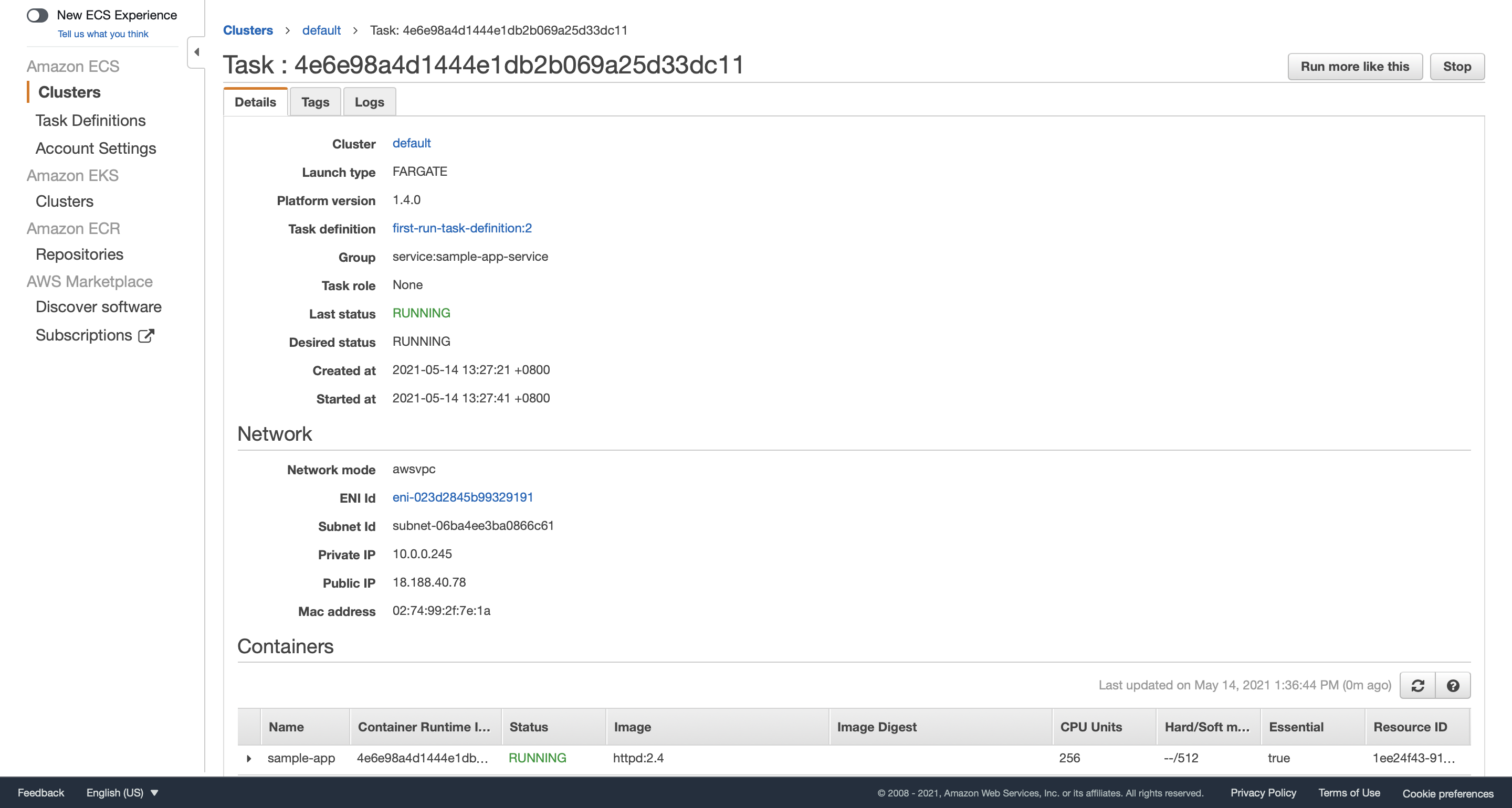
Visit 18.188.40.78 and we will see our sample app running.
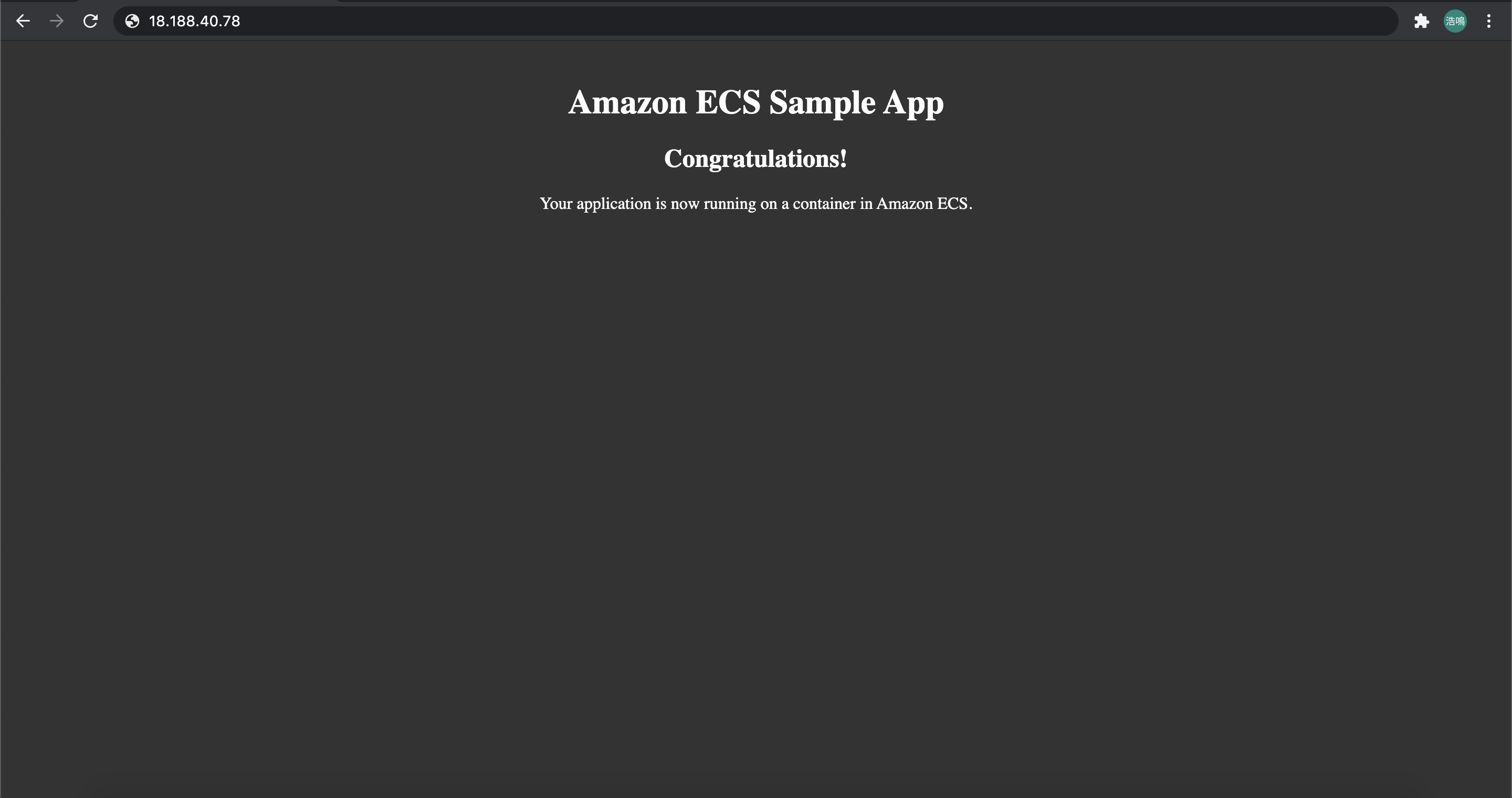
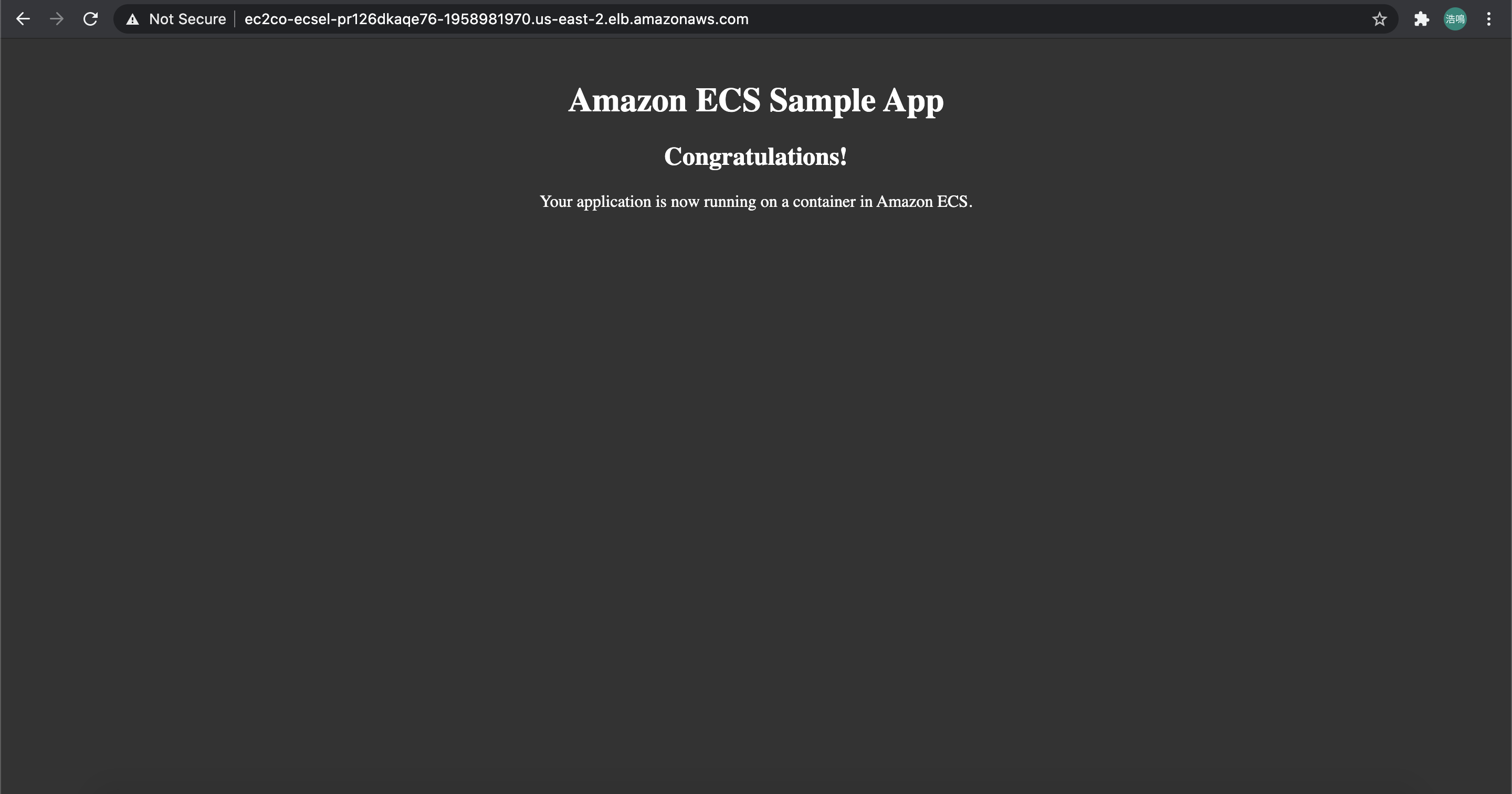
We could also visit our sample app through our Application Load Balancer. Check DNS name of your ALB in the Load Balancer Dashboard:

Visit EC2Co-EcsEl-PR126DKAQE76-1958981970.us-east-2.elb.amazonaws.com:
Optionally, we could enable container auto scaling. By specifying minimum/maximum number of tasks, we are able to adjust number of running tasks dynamically.
The startup template creates a ECS cluster using a CloudFormation stack template. Let’s see what resources it have created for us.
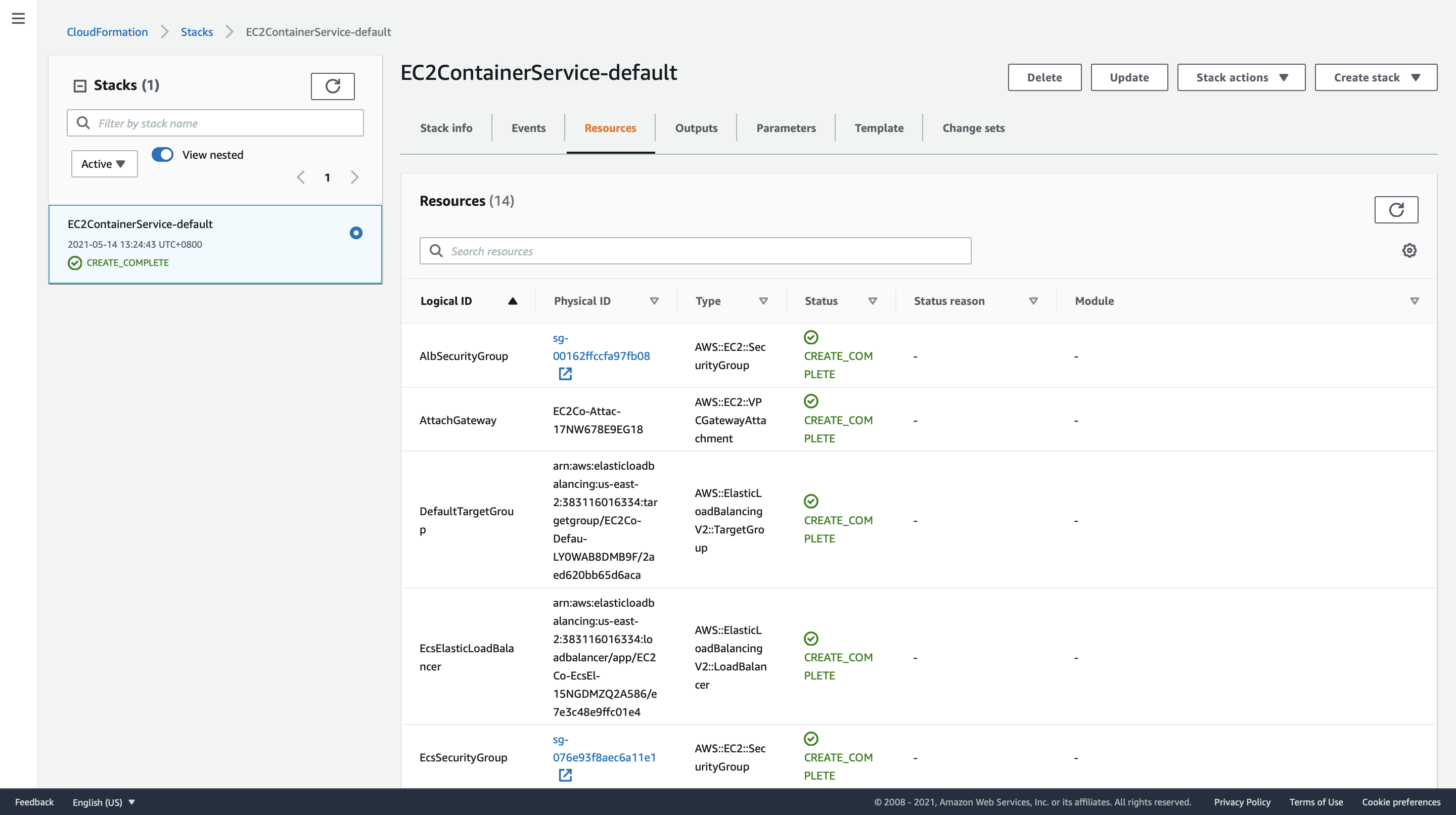
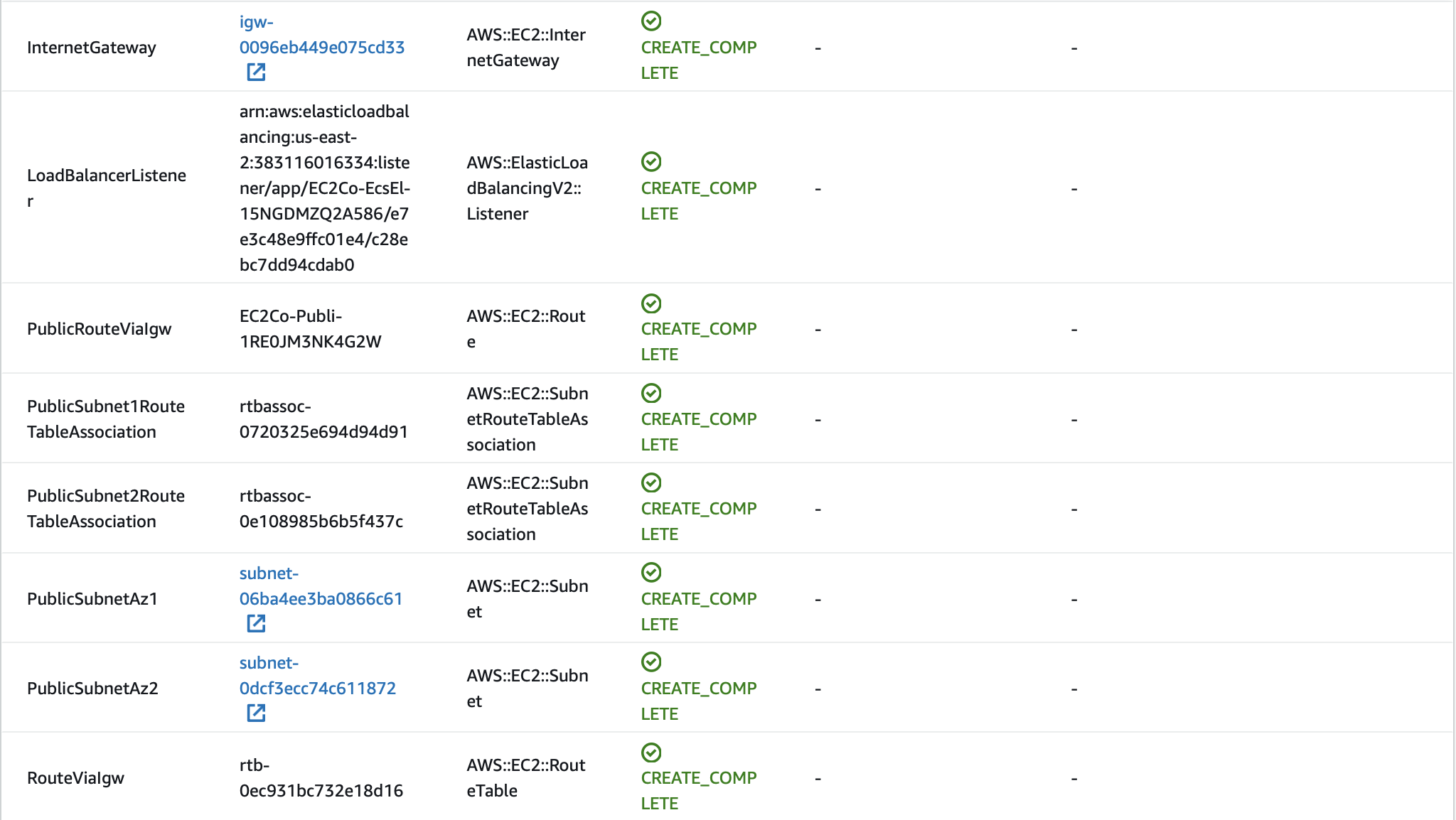

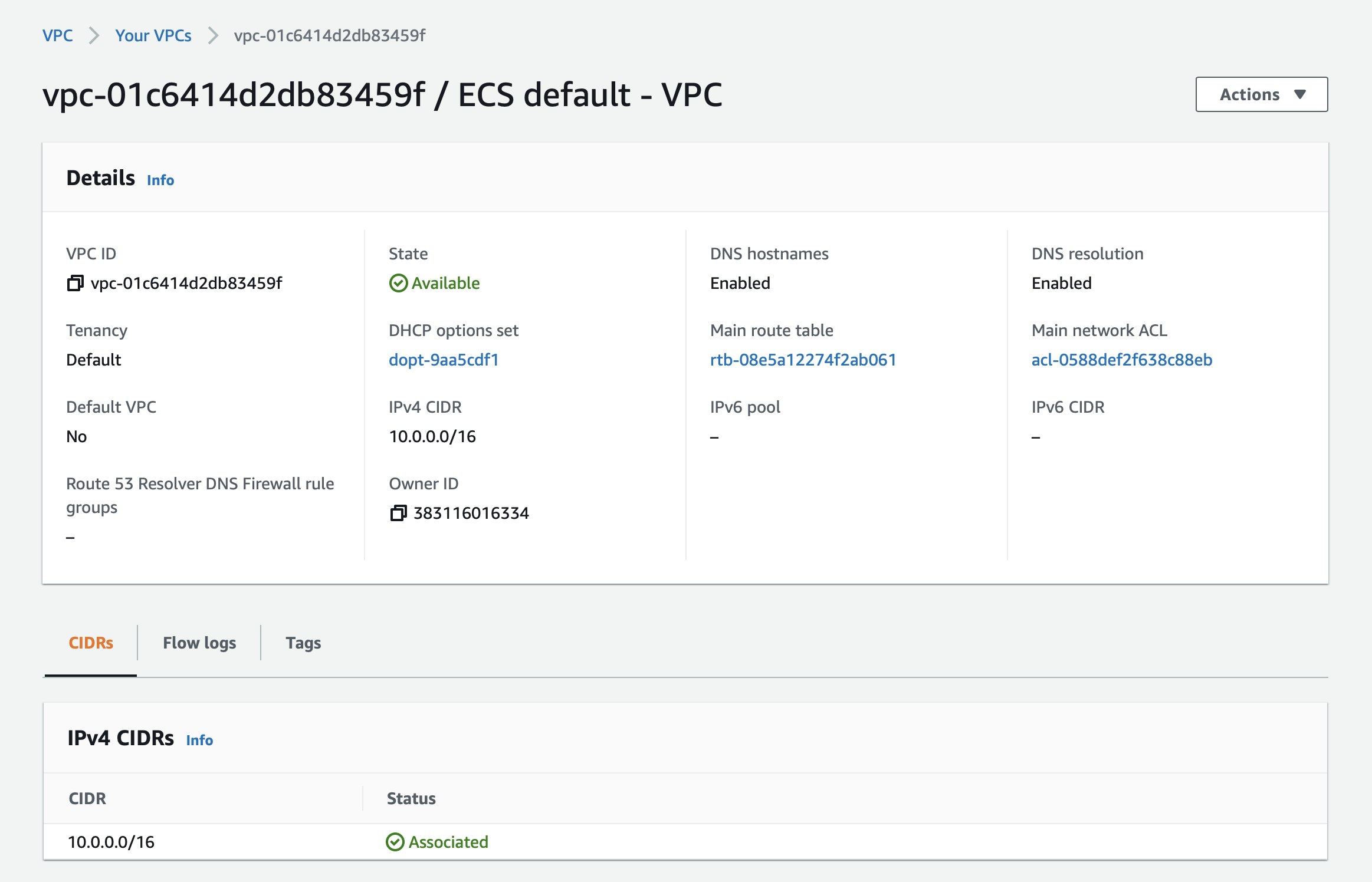
A default VPC for ECS is created:
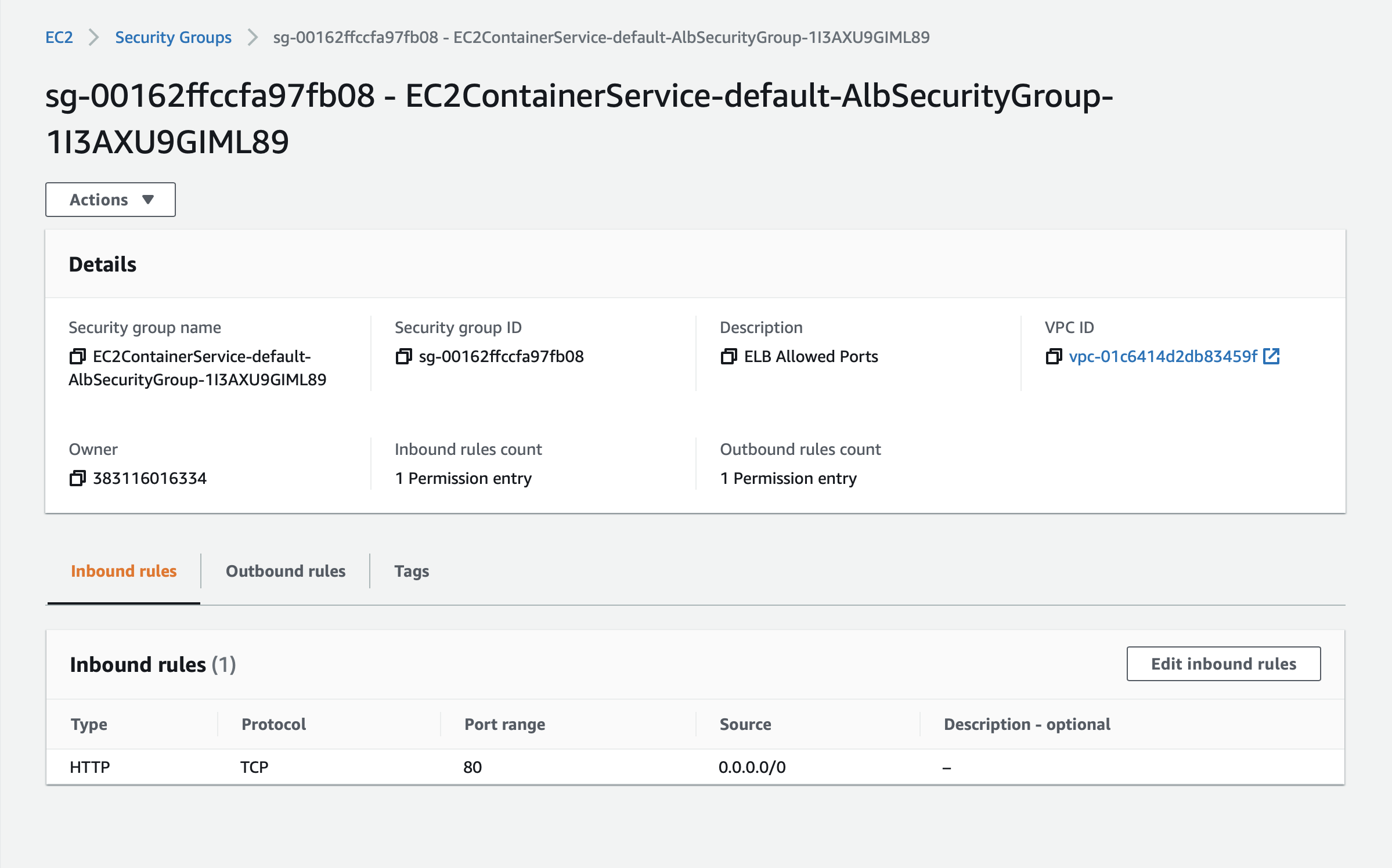
Two security groups are created: an Application Load Balancer security group that allows all traffic on the Application Load Balancer port (HTTP) and an Amazon ECS security group that allows all traffic on the HTTP port or all traffic ONLY from the Application Load Balancer security group.
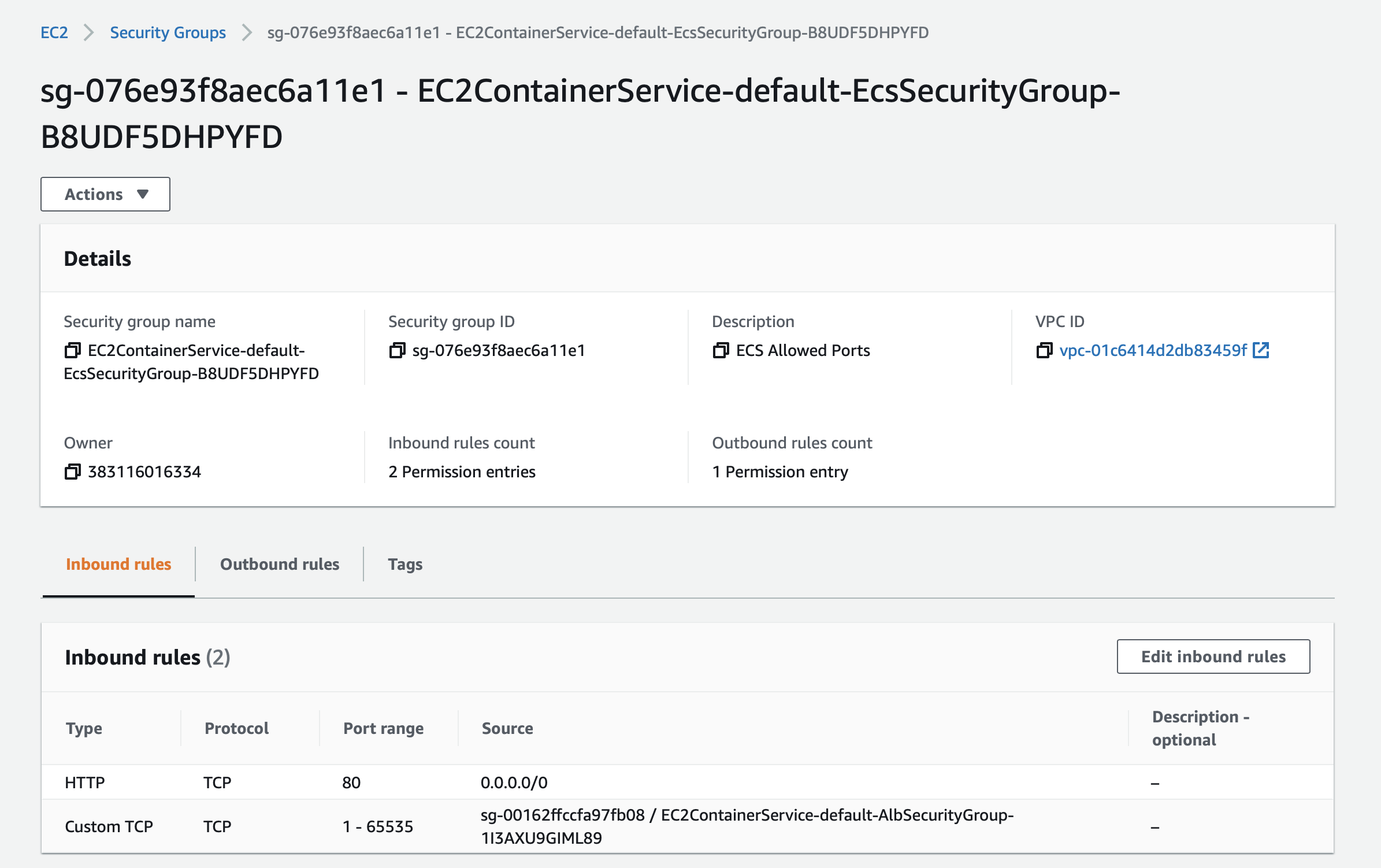
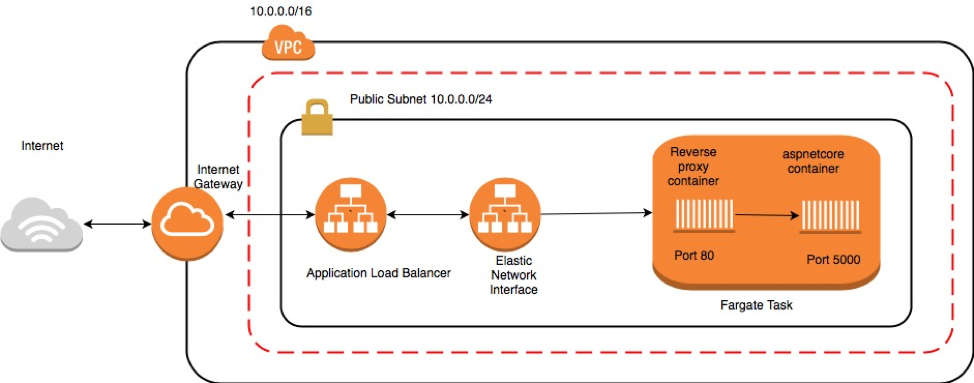
Two subnets, PublicSubnetAz1 (AZ: us-east-2a) and PublicSubnetAz2 (AZ: us-east-2b) in the default VPC are created:
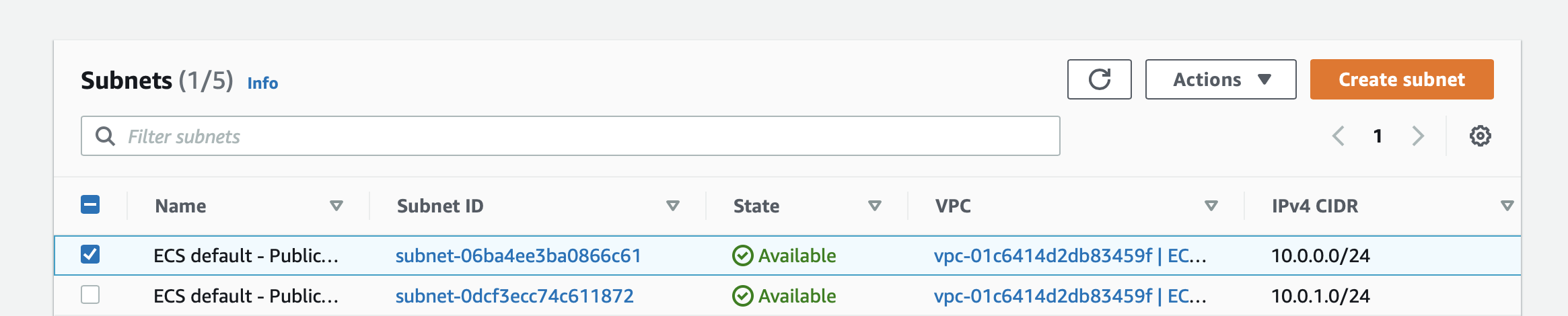
Note that our container is abled to be assigned a public IP because it is in a public subnet, to which an Internet Gatway is attached.
Finally, we could delete the cluster by clicking Delete on the cluster dashboard. This will delete all resources we have created.
Appendix - Using Images on ECR
An Amazon ECS task execution role is automatically created in the Amazon ECS console first-run experience. Thus, we only need to ensure that our ECS owner is as same as our ECR owner in order to pull images successfully.
In Container definition section of the startup template, choose the custom image:
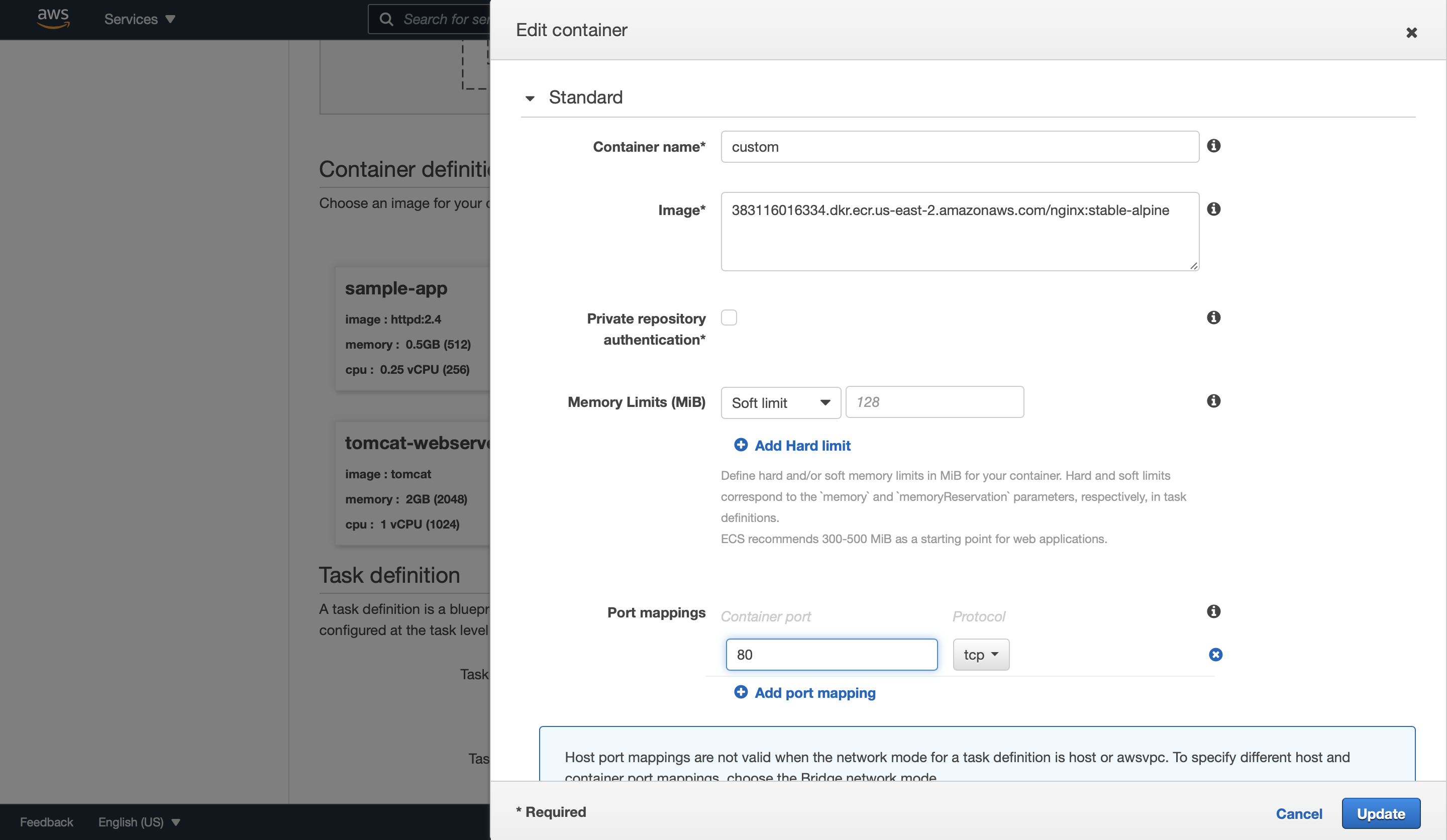
We need to specify port mappings of the container so that the Elastic Load Balancing load balancer knows which ports of the container it should send to.