[AWS] Host a React Application on S3 and CloudFront with Continuous Delievery
We will build a continuous delivery pipeline that deploys a React application to Amazon S3 and syncs it with Amazon CloudFront, a content delivery network (CDN) managed by AWS.
All source codes are available at https://github.com/minghsu0107/sync-react-s3-cloudfront.
Why
It is quite convenient to configure a S3 bucket for static website hosting. However, we can only access it via HTTP protocol. A great way to host our contents is to place it to Amazon CloudFront. This way, not only can we benefit from HTTPS protection but also the out-of-the-box caching mechanism CloudFront provides for us.
Steps
Access Policies
Your IAM user must be attached with proper S3 access policies and the following CloudFront policies.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Action": "s3:ListAllMyBuckets",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::BUCKET"
},
{
"Action": [
"cloudfront:CreateInvalidation",
"cloudfront:GetDistribution",
"cloudfront:GetStreamingDistribution",
"cloudfront:GetDistributionConfig",
"cloudfront:GetInvalidation",
"cloudfront:ListInvalidations",
"cloudfront:ListStreamingDistributions",
"cloudfront:ListDistributions"
],
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
Where BUCKET is a placeholder of your bucket name.
S3 Static Website Hosting
To enable S3 static website hosting, follow these steps.
- Sign in as your IAM user and open the Amazon S3 console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/s3/.
- In the Buckets list, choose the name of the bucket that you want to enable static website hosting for.
- Choose Properties.
- Under Static website hosting, choose Edit.
- Choose Use this bucket to host a website.
- Under Static website hosting, choose Enable.
- In Index document, enter the file name of the index document, typically
index.html. - Upload error page.
- Allow all bucket public access
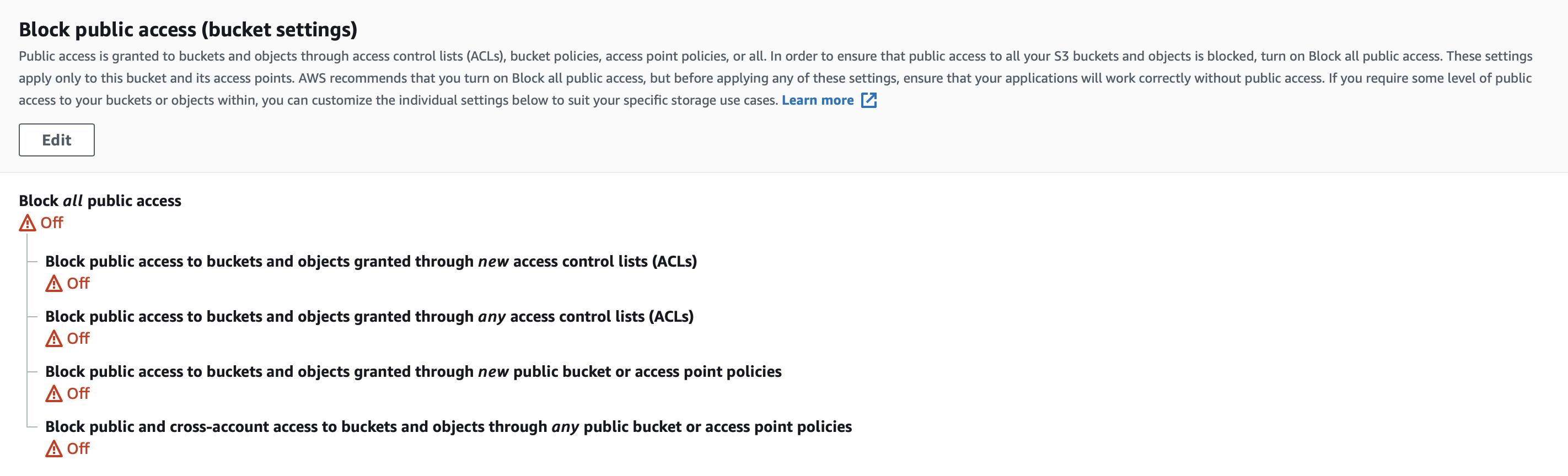
- (optional) Attach bucket policy to grant public read permission on all objects. Or you could grant public read permission during CI flows. We will cover it later.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "PublicReadGetObject",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": "*",
"Action": [
"s3:GetObject"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::sendifybucket/*"
]
}
]
}
CloudFront Configuration
Next, create a CloudFront web distribution. In addition to the distribution settings that you need for your use case, enter the following:
- For Origin Domain Name, enter your s3 static website endpoint. For example,
mybucket.s3-website.us-east-2.amazonaws.com
After the distribution is enabled, visit https://<distribution_id>.cloudfront.net and you will see your website.
Continuous Delivery
We use Drone CI as our automation tool. There are two main steps in the pipeline, which are building React applcation and deploying to AWS.
- Building React application - In this step, we install all dependencies and create a minified bundle to
build/folder.
- name: build-react-app
image: node:15.14
commands:
- npm install && npm run build
- Deploy to AWS - In this step, we upload the minified bundle to S3 and invalidate the CloudFront cache in order to see the updated website instantly.
- name: sync-react-app
image: amazon/aws-cli:2.1.29
environment:
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID:
from_secret: aws_access_key_id
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY:
from_secret: aws_secret_access_key
CLOUDFRONT_DISTRIBUTION_ID:
from_secret: cloudfront_distribution_id
BUCKET:
from_secret: bucket
commands:
- aws s3 sync ./build/ s3://$BUCKET/ --delete --acl public-read
- aws cloudfront create-invalidation --distribution-id $CLOUDFRONT_DISTRIBUTION_ID --paths "/*"
The first command aws s3 sync puts the minify bundle to S3 bucket. The argument --acl public-read grants read permission on our contents to the public. You could ignore this argument if you have enabled public read on all objects via bucket policies mentioned above.
The second command aws cloudfront create-invalidation invalidates CloudFront cache in order that the new version becomes visible.