[K8s] All You Need to Know to Integrate Traefik with Cloud Ingress
Traefik is a powerful ingress controller with easy deployment and configuration. However, cloud providers like AWS and GCP also provide ingress implementations of their managed Kubernetes.
In this post, we will take GCP as example and walk through all needed knowledge of integrating Traefik deployment with ingress provided by GKE. This way, we could enjoy the benefits of feature-rich Traefik CRD as well as convenient infrastruture provisions provided by cloud ingress.
All source codes are available at https://github.com/minghsu0107/traefik-ingress-gke.
Traefik Introduction
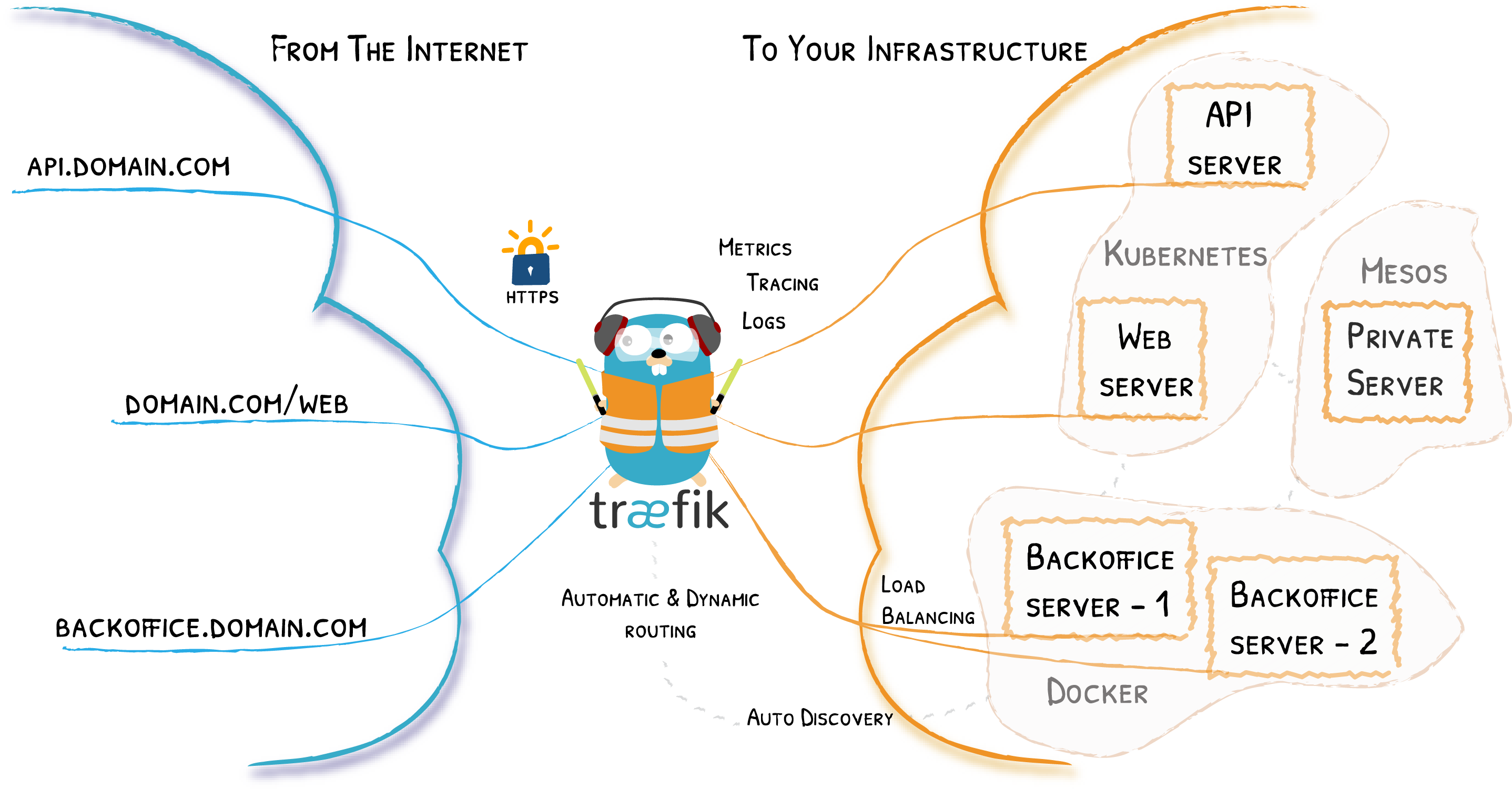
Traefik is an open-source Edge Router that makes publishing your services a fun and easy experience. It receives requests on behalf of your system and finds out which components are responsible for handling them. There are a lot of useful middlewares available, such as regex matching, rate limiting, authentication, and many more. The best part is that Traefik automatically discover new configurations and apply them in real time. For those who are not familiar with Traefik, reading the Traefik documentation is a good start.
Traefik Configuration
In this section, we will cover common configuration of Traefik that is vendor-neutral and compatible with native Kubernetes.
Traefik CRD
Traefik is natively compliant with Kubernetes using the custom resource definitions. Custom resources are extensions of the Kubernetes API, representing a customization of a particular Kubernetes installation. Custom resources help us to declare Traefik components without resorting to lots of ingress annotations.
To start with, let’s create a namespace traefik:
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: traefik
Then deploy Traefik CRDs.
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: ingressroutes.traefik.containo.us
spec:
group: traefik.containo.us
names:
kind: IngressRoute
plural: ingressroutes
singular: ingressroute
scope: Namespaced
version: v1alpha1
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: ingressroutetcps.traefik.containo.us
spec:
group: traefik.containo.us
names:
kind: IngressRouteTCP
plural: ingressroutetcps
singular: ingressroutetcp
scope: Namespaced
version: v1alpha1
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: ingressrouteudps.traefik.containo.us
spec:
group: traefik.containo.us
names:
kind: IngressRouteUDP
plural: ingressrouteudps
singular: ingressrouteudp
scope: Namespaced
version: v1alpha1
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: middlewares.traefik.containo.us
spec:
group: traefik.containo.us
names:
kind: Middleware
plural: middlewares
singular: middleware
scope: Namespaced
version: v1alpha1
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: tlsoptions.traefik.containo.us
spec:
group: traefik.containo.us
names:
kind: TLSOption
plural: tlsoptions
singular: tlsoption
scope: Namespaced
version: v1alpha1
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: tlsstores.traefik.containo.us
spec:
group: traefik.containo.us
names:
kind: TLSStore
plural: tlsstores
singular: tlsstore
scope: Namespaced
version: v1alpha1
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: traefikservices.traefik.containo.us
spec:
group: traefik.containo.us
names:
kind: TraefikService
plural: traefikservices
singular: traefikservice
scope: Namespaced
version: v1alpha1
Next, create a service account traefik-ingress-controller and bind a cluster role to it so that Traefik could use the service account to access custom resources.
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: traefik-ingress-controller
namespace: traefik
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: traefik-ingress-controller
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- services
- endpoints
- secrets
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- extensions
- networking.k8s.io
resources:
- ingresses
- ingressclasses
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- extensions
resources:
- ingresses/status
verbs:
- update
- apiGroups:
- traefik.containo.us
resources:
- middlewares
- ingressroutes
- traefikservices
- ingressroutetcps
- ingressrouteudps
- tlsoptions
- tlsstores
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: traefik-ingress-controller
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: traefik-ingress-controller
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: traefik-ingress-controller
namespace: traefik
Next, deploy Traefik itself using Kubernetes Deployment type.
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
annotations:
prometheus.io/port: http-metrics
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
labels:
app: traefik
name: traefik
namespace: traefik
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: traefik
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: traefik
spec:
serviceAccountName: traefik-ingress-controller
containers:
- name: traefik
ports:
- containerPort: 80
name: web
- containerPort: 8080
name: admin
- containerPort: 8082
name: http-metrics
args:
- --log.level=INFO
- --api
- --api.dashboard
- --api.insecure
- --entrypoints.web.address=:80
- --providers.kubernetescrd
- --metrics.prometheus.entryPoint=metrics
- --entryPoints.metrics.address=:8082
- --accesslog=true
- --ping
- --ping.entryPoint=web
image: traefik:v2.3
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /ping
port: 80
We deploy Traefik in traefik namespace and expose prometheus endpoint at 0.0.0.0:8082/metrics. We also enable readiness probe on 0.0.0.0/ping. This is neccessary because GKE inteprets readiness probe as service health check parameter.
Finally, deploy a NodePort service to expose Traefik deployment.
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
annotations:
prometheus.io/port: "8082"
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
labels:
app: traefik
name: traefik
namespace: traefik
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- name: web
port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
- name: http-metrics
port: 8082
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8082
selector:
app: traefik
Deploy to Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE)
Instead of directly enabling external load balancer on Traefik service, we handle external traffic by GKE ingress and proxy it to internal Traefik router by HTTP. This way, we could benefit from L7 load balancer features, such as managed certificates and HTTPS redirection, of our ingress instance without modifying any Traefik configuration. The routing now would be like Ingress -> Traefik -> App.
Note that your GKE cluster needs to be running at least a recent version 1.17-gke for this to work.
First, create a static reserved ip address going by the name of traefik-ip.
gcloud compute addresses create traefik-ip --global
Then, deploy an ingress annotated with managed certificate and HTTPS redirection.
---
apiVersion: networking.gke.io/v1
kind: ManagedCertificate
metadata:
name: traefik-cert
spec:
domains:
- mydomain.com
- api.mydomain.com
---
apiVersion: networking.gke.io/v1beta1
kind: FrontendConfig
metadata:
name: traefik-frontend-cfg
namespace: traefik
spec:
redirectToHttps:
enabled: true
responseCodeName: PERMANENT_REDIRECT
---
kind: Ingress
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: myingress
namespace: traefik
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.global-static-ip-name: "traefik-ip"
networking.gke.io/v1beta1.FrontendConfig: "traefik-frontend-cfg"
networking.gke.io/managed-certificates: "traefik-cert"
spec:
backend:
serviceName: traefik
servicePort: 80
Above configuration creates a managed certficate on domains mydomain.com and api.mydomain.com. Google Cloud provisions managed certificates valid for 90 days. About one month before expiry, the process to renew your certificate automatically begins. Our ingress instance will use this certificate to handle HTTPS requests. Also, we have set up automatic HTTPS redirection using native GKE resource FrontendConfig.
Conclusion
In this post, we have covered details on deploying Traefik to GKE while having it integrated with GKE-native ingress. Such combination helps us decouple Traefik components from cloud ingress features like certificate management and HTTPS redirection, increasing the overall maintainability.